Islam Mohamed
KagNet: Knowledge-Aware Graph Networks for Commonsense Reasoning
Summary
- A proposed Knowledge-aware reasoning framework is , which mainly has the following two steps:
- schema graph grounding (see picture below)
- graph modeling for inference
- The core is the GCN-LSTM-HPA structure:
- Composed of GCN, LSTM, and hierarchical path-based attention mechanism
- Used for path-based relational graph representation
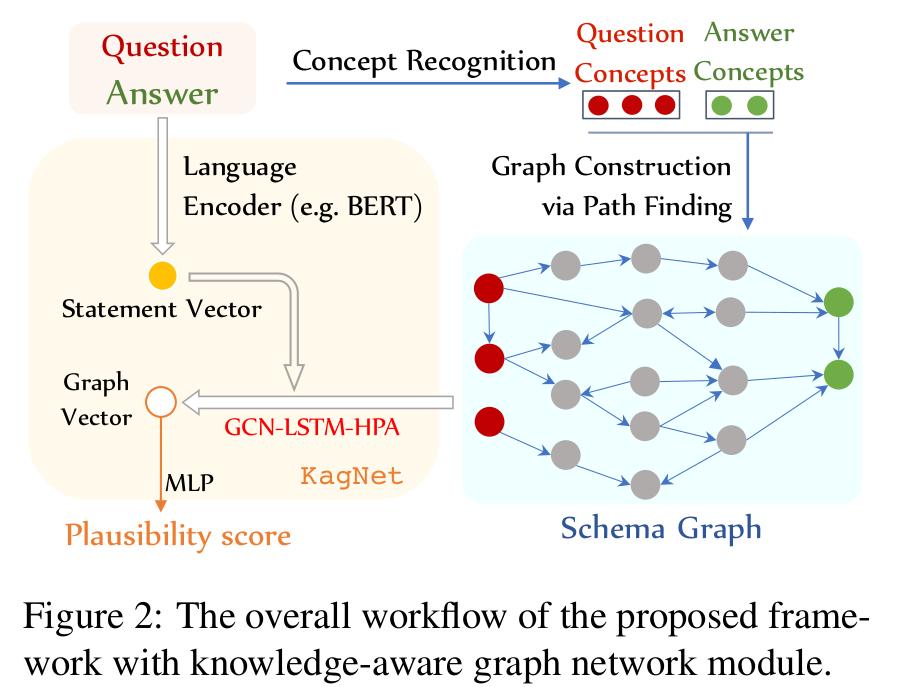
- The overall workflow of the KAGNET module:
- First, identify the concepts in Q and A, find the path between them based on these concepts, and construct a (ground) schema graph.
- Use LM encoder to encode QA pairs to generate statement vector S, which is used as the input of GCN-LSTM-HPA to calculate graph vector G.
- Finally, use graph vector to calculate the final QA pair score.
Model
Schema Graph Grounding
Concept Recognition
- A simple and rude way is to match the n-gram in the sentence with the concept in the knowledge graph.
- For example, in the question “Sitting too close to watch tv can cause what sort of pain?”, the result of problem concept matching is {sitting, close, watch_tv, watch, tv, sort, pain, etc.}.
- The author uses some rules to enhance this simple method, for example, using lemmatization (lemmatization: remove the affix of the word, extract the main part of the word.
- For example, the word “cars” after lemmatization is “car”
- The word “ate” after morphological restoration is “eat”)
- soft matching and stop word filtering
Schema Graph Construction
- The author passes in all the concepts (question concepts and answer concepts).
- Use the path finding method to construct a sub-graph of the entire knowledge graph to represent the knowledge concepts and edges related to the question-answer pair reasoning.
- For every problem concept And answer concept, The author can find a path between two concepts that passes less than k (the author set it to 4 in the experiment to obtain a three-hop path).
- After that, the author adds the concept-to-existence side between the question concept and the answer concept.
Path Pruning via KG Embedding
- The author uses knowledge graph embedding technology such as TransE to pre-train concept embedding V And relation type embedding R.
- The author scored each path by decomposing it into a set of triples, the confidence of which can be directly measured by the scoring function of the KGE method (i.e. the confidence of triple classification).
- Thus, we score a path with the multiplication product of the scores of each triple in the path, and then we empirically set a threshold for pruning.
Knowledge-Aware Graph Network
Graph Convolutional Networks
- Use GCN to update the concept vector with the help of neighboring nodes helps to eliminate ambiguity and further obtain context-based concept embedding.
- GCN can capture the structural characteristics of the schema graph to help reasoning.
- For example, a shorter and tighter connection between the question and the answer concept may mean that it is more reasonable in a specific text.
- The author apply GCN to the plain version (unlabeled, non-directional) of the schema graph, ignoring the type of relationship on the side.
- For schema graph g Concepts vectors is initialized with the pre-trained vector obtained by the previous KGE method (TransE).
- After the first ( L+1 ) Layer iteratively update the concept vector, the input is the set of neighboring nodes [N of i ].
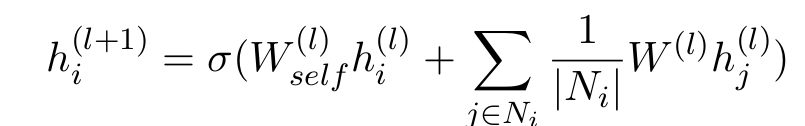
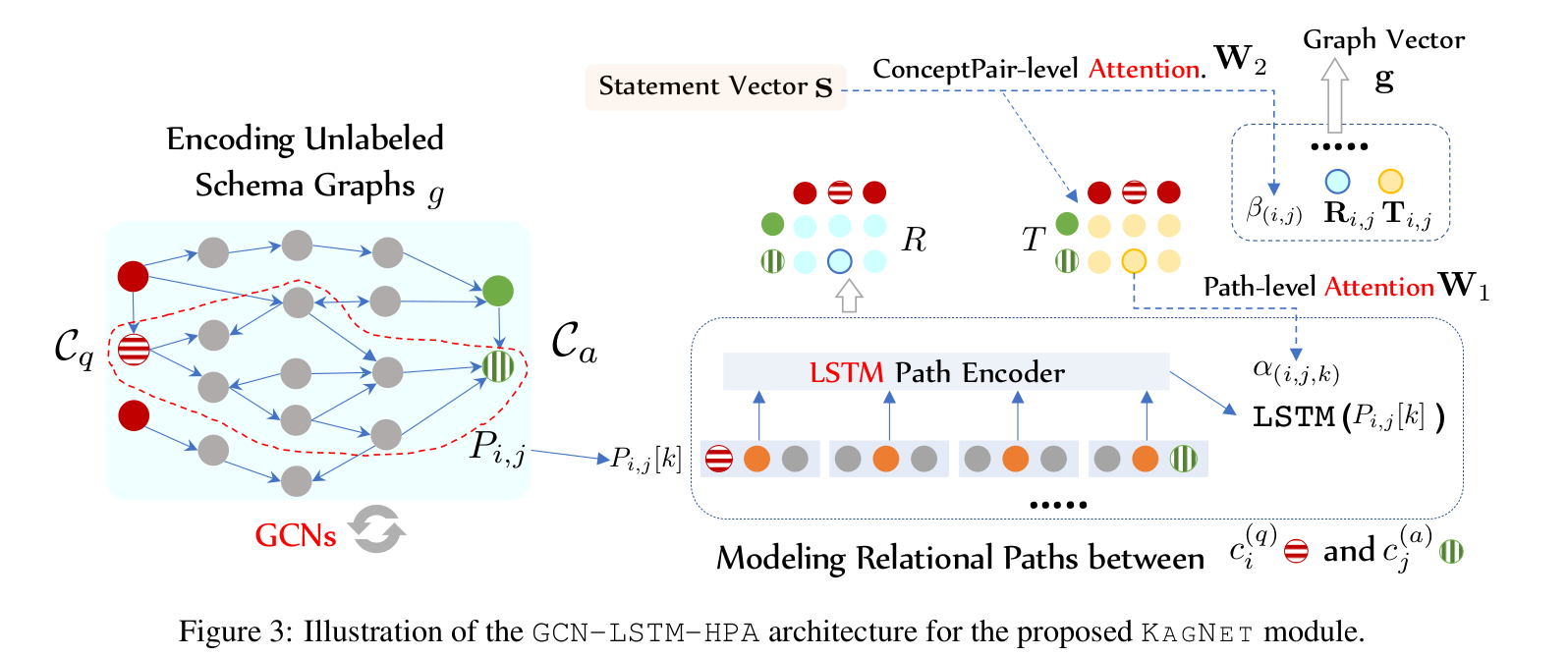
Relational Path Encoding
- Use P i,j [k] to represent the k-th path between the i-th question concepts and the j-th answer concept.
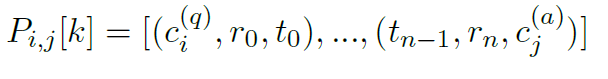
- Use LSTM to encode a sequence of triple vectors to get the path vector
- R i,j can be can be viewed as the latent relation between the question concept and the answer concept, for which we aggregate the representations of all the paths between them in the schema graph.
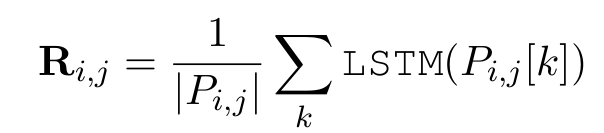
- S can be obtained from the encoder of the language model (LSTM or GPT/BERT).
- The T i,j is inspired from the Relation Network which also encodes the latent relational information yet from the context in the statement s instead of the schema graph g.
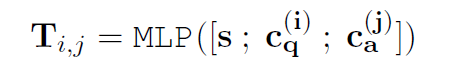
- Use average pooling to get the graph vector
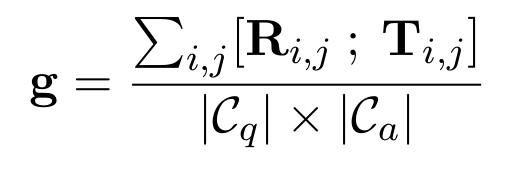
- Finally, score between 0 and 1 is performed to determine whether a candidate answer in the question is reliable:
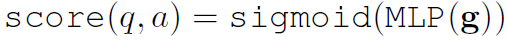
Hierarchical Attention Mechanism
- Choose more important paths and concepts.
- Path level attention:
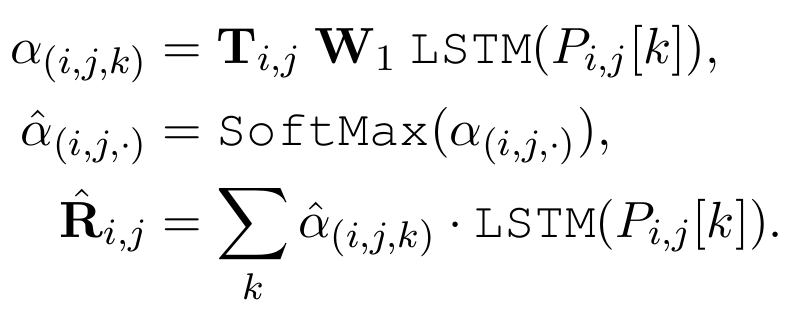
- Concept pair level attention:
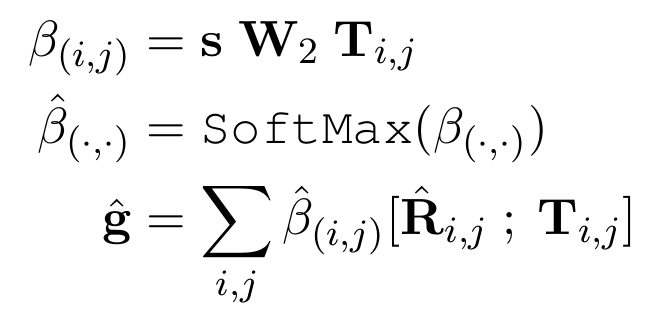
Error Analysis
- negative reasoning
- graph grounding is not sensitive to negative words
- comparative reasoning strategy
- No comparison between answers
- subjective reasoning
- Some answers are based on subjective reasoning
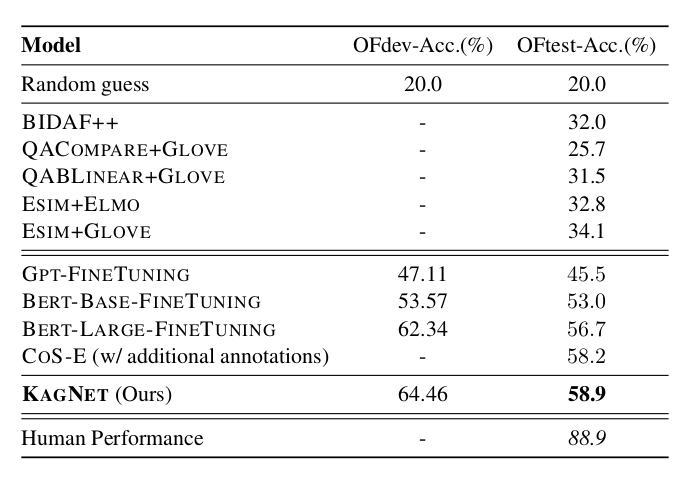
Results
- Results on csqa Dataset
Refrences
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/92141033
- http://xingluxi.github.io/2019/09/09/paper-emnlp2019-kagnet/
Feel free to share!