Islam Mohamed
Fusing Context Into Knowledge Graph for Commonsense Question Answering
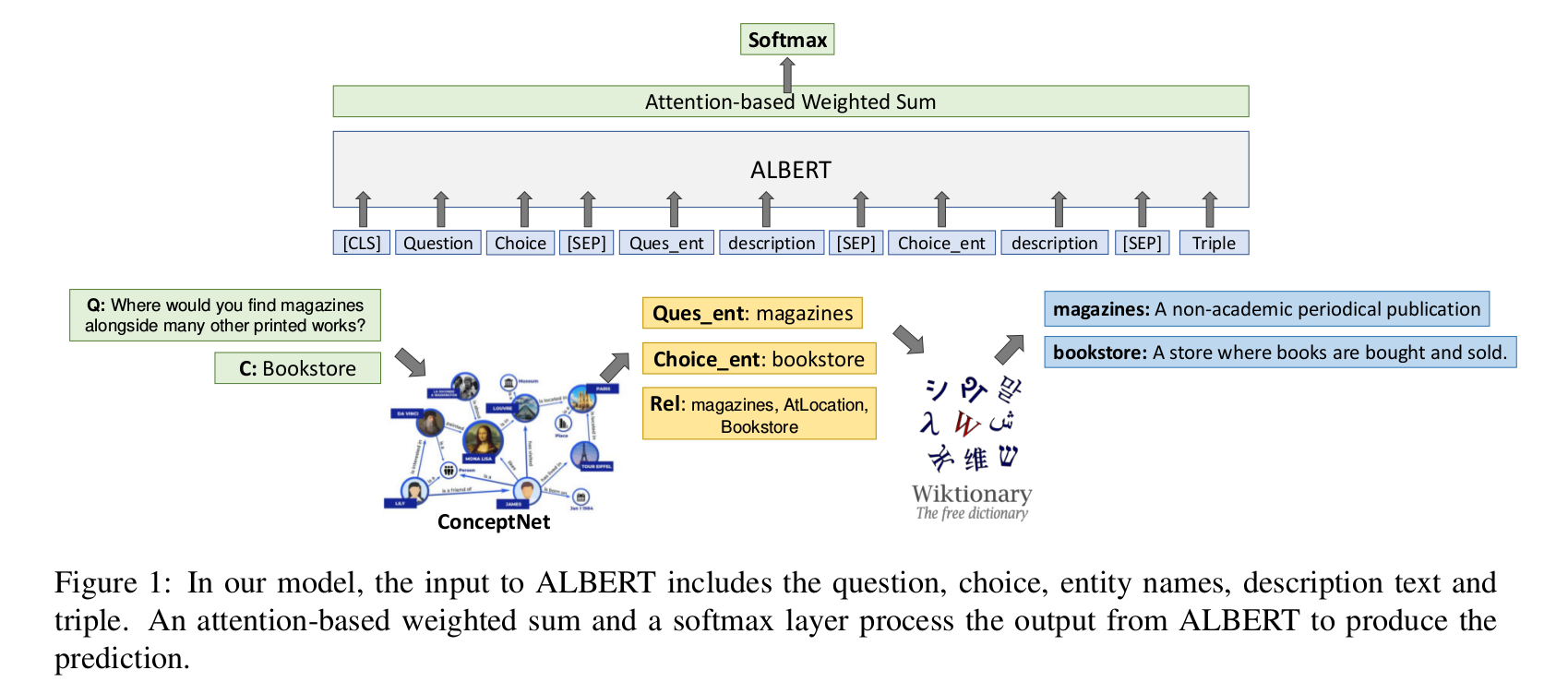
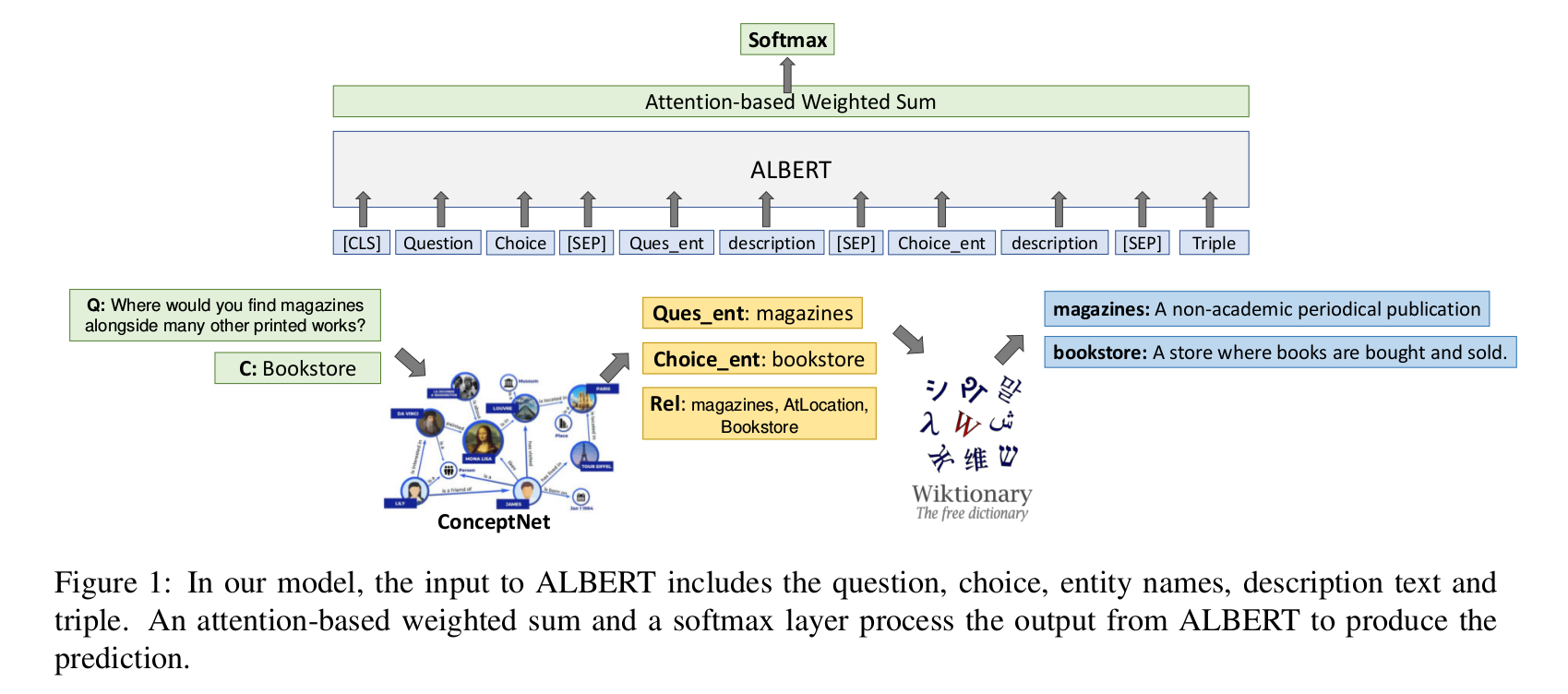
Method
Knowledge Retrieval
- Suppose the question mentions an entity Eq ∈ V and the choice contains an entity Ec ∈ V. W
- We then employ the KCR method to select relation triples.
- If there is a direct edge r from Eq to Ec in G, we choose this triple (Eq , r, Ec).
- Otherwise, we retrieve all the N triples containing Ec.
- Each triple j is assigned a score Sj which is the product of its triple weight Wj provided by ConceptNet and relation type weight T of r and j:
- Here, Rj is the relation type of the triple j, and N of r and j is the number of triples among the retrieved triples that have the relation type r of j .
- In other words, this process favors rarer relation types.
- Finally, the triple with the highest weight is chosen.
Contextual information
- Without additional context, it is hard for the language model to understand its exact meaning, especially for proper nouns.
- Therefore, we leverage large-scale online dictionaries to provide definitions as context.
- We use a dump of Wiktionary which includes definitions of 999,614 concepts.
- For every concept, we choose its first definition entry in Wiktionary as the description.
- For every question/choice concept, we find its closest match in Wiktionary by using the following forms in order:
- original form
- lemma form by Spacy
- base word (last word).
- For example, the concept “taking notes” does not appear in its original form in Wiktionary, but its lemma form “take notes” is in Wiktionary and we get its description text: “To make a record of what one hears or observes for future reference”.
- In this way, we find descriptions of all entities in our experiments.
- Finally, we feed the question, choice, descriptions and triple into the ALBERT model in the followin format:
- [CLS] Question : choice : [SEP] : entity question : desciption : [SEP] : entity choice : desciption : [SEP] : triple.
Reasoning
- On top of ALBERT, we leverage an attention-based weighted sum and a softmax layer to generate the relevance score for the question-choice pair.
- In detail, suppose the output representations of ALBERT is (x0 , …, xm ).
- We compute a weighted sum of these embeddings based on attention.
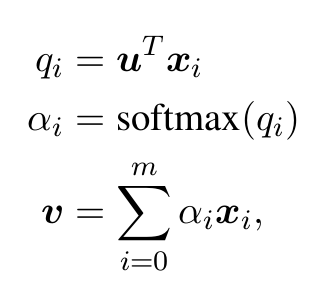
- where u is a parameter vector.
- The relevance score between the question and the choice is then s = softmax(v tranpose * b), where b is a parameter vector and the softmax is computed over all choices for the cross-entropy loss function.
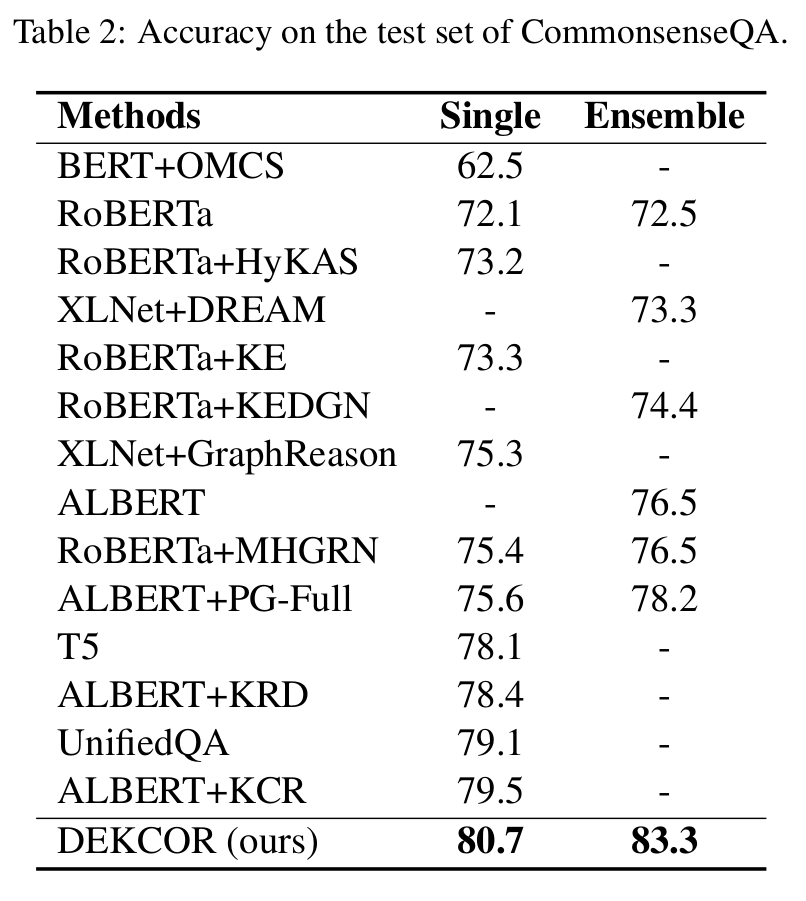
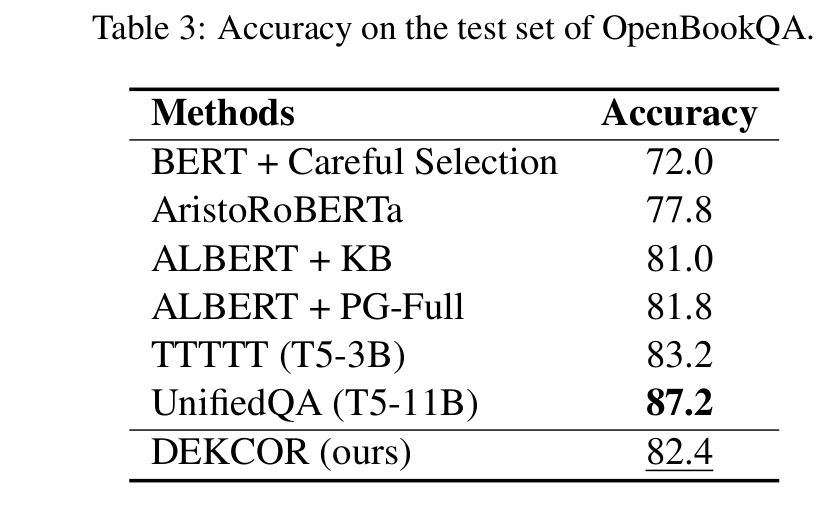
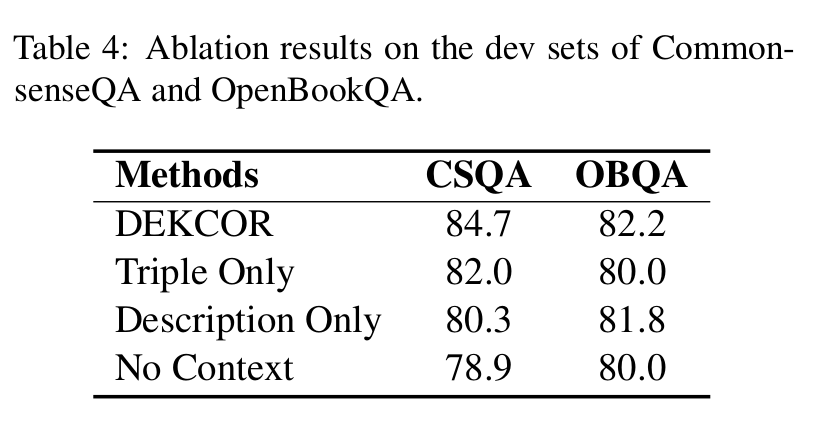
Results
Reference
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.04808
Feel free to share!